Integrating Orbital Stretch Wrappers into Existing Conveyor Systems?
Leading paragraph:
You have a smooth, efficient conveyor system moving your steel coils or wire rods. Then, the product reaches the end of the line. Everything stops. Workers scramble to manually wrap, secure, and label each load. This bottleneck is not just slow; it's expensive and dangerous. The pressure to keep up with production targets while managing safety and costs is immense. If this scene feels familiar, you are not alone. Many factory managers face this exact challenge at the critical junction where production meets packaging.
Integrating an orbital stretch wrapper directly into your existing conveyor line is the definitive solution to eliminate this bottleneck. This automated approach creates a seamless, continuous flow from production to shipping, dramatically boosting throughput, enhancing safety, and protecting your product investment. (automated packaging integration, conveyor line bottleneck solution)
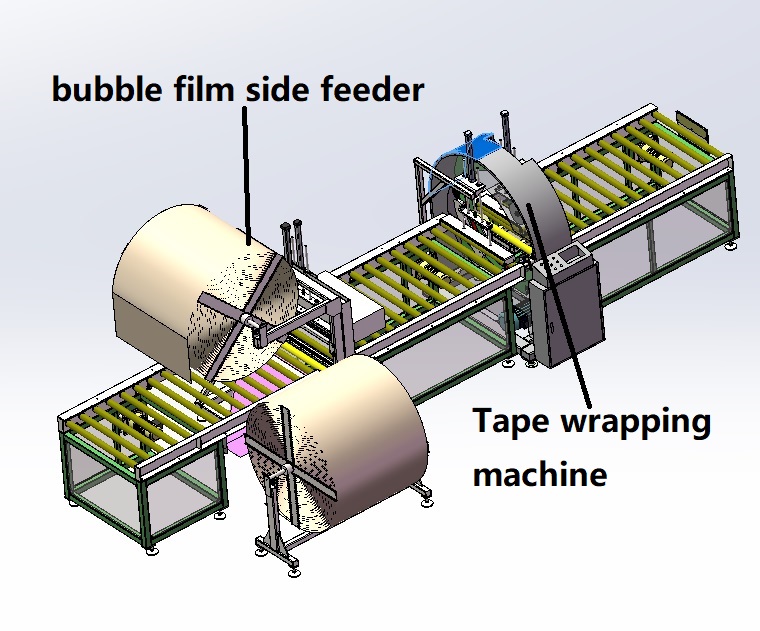
Transition Paragraph:
But how do you make this integration work? Simply buying a machine is not enough. A successful integration requires careful planning around your specific layout, product flow, and operational goals. As someone who has built factories from the ground up, I understand that the devil is in the details. Let's break down the key questions you need to ask to ensure your investment pays off from day one.
1. What are the critical pre-installation checks for a smooth integration?
Leading paragraph:
Imagine the new machine arrives, but it doesn't fit. Or it fits, but it causes a jam upstream. This nightmare scenario wastes time and money. To avoid it, you must conduct thorough pre-installation due diligence. This step is about measuring twice and cutting once, ensuring the physical and operational marriage between your old system and the new wrapper is perfect.
Before installation, you must verify three core aspects: the physical dimensions and floor space, the compatibility of load transfer methods, and the synchronization with your line's control logic and speed. (pre-installation checklist for packaging machinery, conveyor system compatibility)
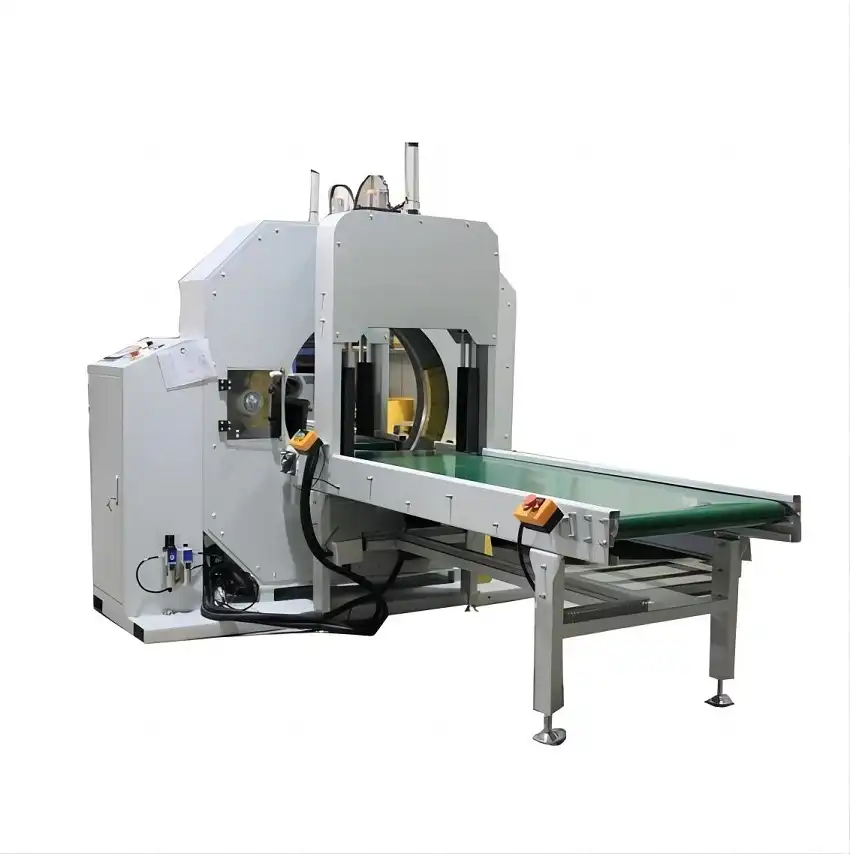

The Three Pillars of Pre-Installation Success
A failed integration often stems from overlooked basics. Let's dive deeper into each critical check.
📏 Pillar 1: Spatial & Dimensional Analysis
This is the most fundamental step. You need a precise map of your production floor.
- Footprint & Clearance: Measure the exact footprint of the orbital wrapper, including all moving parts and service access areas. Don't forget overhead clearance for the rotating ring.
- Conveyor Height & Alignment: The wrapper's infeed and outfeed conveyors must perfectly match the height and width of your existing line. A mismatch of even a few centimeters can cause products to jam or fall.
- Utilities Access: Confirm the location of power sources, compressed air lines, and network points for the new machine. Long, messy cable runs are a safety hazard.
🔄 Pillar 2: Load Transfer Mechanism Compatibility
How will the product move from your line into the wrapper? This is a make-or-break detail.
- Roller Conveyor Integration: This is common. Ensure the roller pitch, diameter, and load capacity are compatible. You may need a transition section.
- Chain Transfer or Pallet-Based Systems: For heavier coils, a chain transfer system might be used. The wrapper's turntable or receiving bed must be designed to interface seamlessly with this mechanism.
- Manual vs. Automated Transfer: The goal is full automation. The integration point should require zero manual intervention to push or guide the load.
⚙️ Pillar 3: Control System & Throughput Synchronization
The machines must "talk" to each other and work at the same pace.
- PLC Communication: Can the wrapper's PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) receive signals from your main line? It needs to know when a load is in position to start wrapping.
- Cycle Time Matching: The wrapper's cycle time (load, wrap, unload) must be equal to or faster than the pace of your upstream production. If the wrapper is slower, it becomes the new bottleneck.
- Emergency Stop Integration: The wrapper's E-stop must be integrated into your plant's overall safety circuit. If someone hits a stop button upstream, the wrapper must also halt immediately.
| Table: Pre-Installation Checklist Summary | Check Category | Key Questions to Answer | Common Pitfall to Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Space & Layout | Is there enough room for the machine and service access? Do heights align? | Assuming the space is sufficient without accounting for the full rotation arc. | |
| Mechanical Interface | How will the load transfer work? Are rollers/chain drives compatible? | Using makeshift ramps or guides that cause product damage or jams. | |
| Control & Safety | Can the machines communicate? Are cycle times synchronized? Are E-stops linked? | Having an isolated machine that operators must start/stop manually, killing efficiency. |
Neglecting these checks is the fastest way to turn an efficiency project into a costly disruption. A reliable partner like Fengding excels at conducting this audit with you, using their experience to foresee issues you might miss. (factory floor planning for automation, PLC synchronization for packaging line)
2. How do you choose the right orbital wrapper for your specific line?
Leading paragraph:
Orbital wrappers are not one-size-fits-all. Choosing the wrong model is like putting a sports car engine in a dump truck—it might work, but it won't be efficient or durable. Your choice must be dictated by your product, your line's environment, and your production volume. A mismatch here leads to underperformance, frequent breakdowns, and wasted capital.
The right orbital wrapper is chosen based on a clear analysis of your product dimensions and weight, the required wrapping pattern and film type, and the desired level of automation and data connectivity for your operation. (how to choose an orbital stretch wrapper, industrial packaging machine selection)
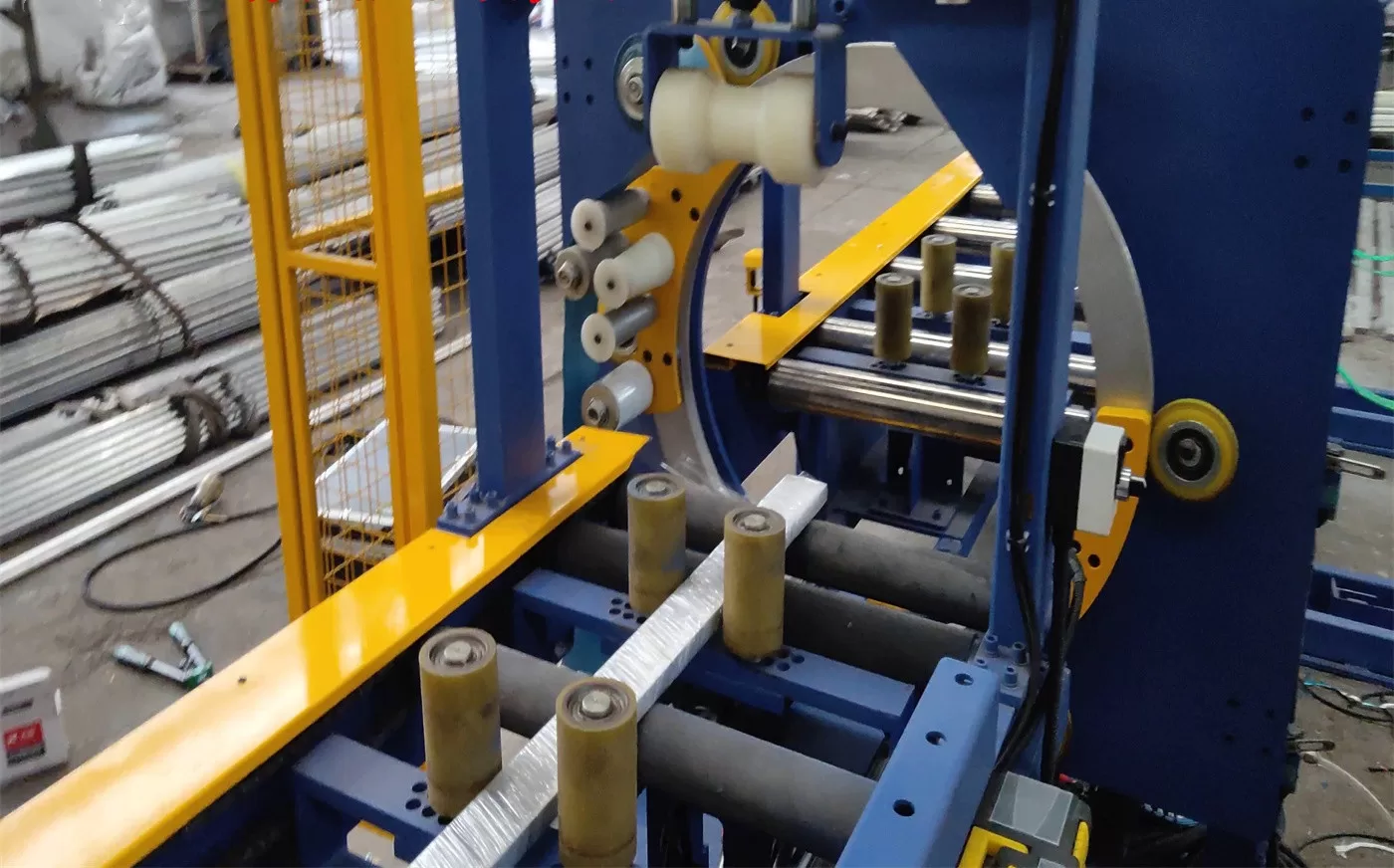

Matching the Machine to Your Mission
Let's deconstruct the selection process into actionable criteria.
🎯 Criterion 1: Product Profile (The "What")
Your product dictates the machine's core specifications.
- Size & Weight Range: What is the diameter, width, and weight of your coils or bundles? The machine must have a turntable or mandrel with adequate capacity and size.
- Product Stability: Is the product uniform, or does it have irregular shapes? This affects the need for top platen pressure or side guides to stabilize the load during wrapping.
- Surface Sensitivity: Are you wrapping polished stainless steel or rough hot-rolled coil? This determines if you need a non-marking film carriage or special protective layers like bubble film.
🔁 Criterion 2: Wrapping Process (The "How")
How you need to protect the product defines the wrapper's capabilities.
- Film Type & Layers: Standard polyethylene stretch film? Or do you require a multi-layer system with a first layer of waterproof paper or bubble film, followed by a reinforcing stretch film? Machines from leaders like Fengding often offer this multi-film capability.
- Wrap Pattern & Tension: A simple spiral wrap might suffice for internal storage. For overseas shipping, you may need a reinforced "belt and braces" pattern with extra layers on the edges. Precise, programmable film tension is crucial to prevent crushing or loose wraps.
- Speed Requirements: How many units per hour do you need to wrap? This defines the required cycle time and influences the drive system's power.
🤖 Criterion 3: Automation & Intelligence (The "Future")
Your wrapper should solve today's problems and be ready for tomorrow's smart factory.
- Integration Readiness: Does it have standard I/O (Input/Output) ports and communication protocols (e.g., Profibus, Ethernet/IP) for easy PLC integration?
- Data Collection: Can it provide data on film usage, cycle counts, and error logs? This is vital for OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) tracking and predictive maintenance.
- Ease of Use: Is the HMI (Human-Machine Interface) intuitive? Can operators easily change recipes for different product sizes?
Choosing based on price alone is a trap. A slightly more expensive, robust machine from a proven manufacturer will have a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to higher uptime and longer life. Wuxi Buhui is another reputable manufacturer known for solid engineering in this space. The goal is to find a partner whose machine is engineered for your specific "how," not just sold as a generic solution. (industrial coil wrapping specifications, smart packaging machine features)
3. What are the common integration challenges and how to solve them?
Leading paragraph:
Even with perfect planning, challenges will arise during integration. These are the moments that test the mettle of both your team and your equipment supplier. Common issues like misalignment, control hiccups, or workflow disruptions can derail the project. But forewarned is forearmed. Knowing these challenges allows you to proactively develop solutions.
The most common integration challenges include mechanical misalignment causing jams, control system communication failures, and workflow disruptions during the cut-over from old to new processes. Each requires a systematic troubleshooting approach. (packaging line integration problems, industrial automation challenges)

Navigating the Integration Hurdles
Let's examine these challenges and their practical solutions.
⚠️ Challenge 1: Mechanical & Spatial Issues
The physical integration is the first hurdle.
- Symptom: Product jams at the transfer point, inconsistent wrapping due to misaligned entry.
- Root Causes: Incorrect height measurements, worn conveyor rollers on the existing line, or insufficient guiding systems.
- Solution: Use laser alignment tools for precision. Install adjustable transition plates or guide rails. Often, the existing conveyor section leading into the wrapper needs refurbishment or replacement to meet the new system's standards. A good supplier will include this assessment in their proposal.
📶 Challenge 2: Control System & Communication Hiccups
The machines are physically connected but not "talking" properly.
- Symptom: The wrapper doesn't start automatically, or it starts at the wrong time, causing collisions or gaps in the line.
- Root Causes: Mismatched voltage signals (e.g., 24V DC vs. 120V AC), incorrect wiring of sensor inputs, or programming errors in the PLC logic.
- Solution: This is where a supplier's technical expertise is critical. They should provide detailed wiring diagrams and work with your electricians. A joint commissioning period is essential. Start with simple manual trigger signals and gradually build up to full automated sequence testing.
🔄 Challenge 3: Workflow & Human Factor Disruption
The new technology changes how people work, which can cause resistance or errors.
- Symptom: Operators bypass the new system, productivity drops initially, or new safety hazards emerge.
- Root Causes: Lack of training, fear of job loss, or unclear new standard operating procedures (SOPs).
- Solution: Involve your frontline team from the early planning stages. Develop clear, visual SOPs together. Conduct thorough, hands-on training before go-live. Emphasize how the machine removes dangerous tasks and makes their jobs easier and safer. Plan a phased cut-over, if possible, to minimize production impact.
The difference between a good supplier and a great one is visible here. A great supplier like Fengding doesn't just drop off the machine. Their engineers stay on-site through commissioning, actively solving these problems with you. They see the integration through your eyes, understanding that their machine's success is tied to your line's uninterrupted flow. (troubleshooting automated systems, packaging machine commissioning process)
4. How do you calculate the true ROI of an integrated wrapping system?
Leading paragraph:
As a factory manager, every investment must be justified. You need hard numbers to present to management. The price tag of an orbital wrapper is clear, but the true cost is in the ongoing inefficiency it replaces. Calculating ROI isn't just about the machine cost; it's about quantifying the silent costs of your current manual process that are draining your profits every day.
The true ROI is calculated by quantifying and comparing the ongoing costs of your current manual packaging process against the one-time investment and lower operating costs of an automated, integrated orbital wrapping system. (ROI calculation for packaging automation, cost of manual vs automated packing)
Building Your ROI Business Case
Move beyond guesswork. Build your calculation on these tangible factors.
💸 Category A: Costs of Your Current Manual Process (The "Cost of Doing Nothing")
These are the hidden expenses you pay daily.
- Direct Labor Costs: Calculate the fully burdened cost (wages, benefits, insurance) of all workers involved in manual wrapping, securing, and labeling. How many shifts? How many workers per shift?
- Product Damage & Rejection: Track the financial loss from edge damage, scratches, or contamination during manual handling and wrapping. Include costs of rework, customer returns, and lost reputation.
- Workplace Injury Costs: Account for workers' compensation claims, insurance premiums, lost productivity, and potential regulatory fines related to manual handling of heavy loads.
- Inconsistency & Waste: Measure the cost of film/strap overuse, inconsistent application leading to in-transit damage, and the time lost due to variable worker speed.
- Bottleneck Cost: What is the value of the production time lost while finished goods wait to be wrapped? Could the line run faster if this bottleneck were removed?
📊 Category B: Costs & Savings of the Automated System
This is the investment and its payback.
- Capital Investment: The total cost of the orbital wrapper, installation, and any conveyor modifications.
- Operating Costs: Typically much lower. Include electricity, scheduled maintenance, and film consumption (which is often lower due to precise pre-stretch).
- Quantifiable Savings:
- Labor Savings: Reduced number of workers needed on the packaging station.
- Damage Reduction: Projected decrease in product loss.
- Throughput Increase: Value of additional units shipped per day/week.
- Safety Cost Avoidance: Reduced insurance and injury-related costs.
Example ROI Thought Process:
If your manual process costs $150,000 per year in labor, damage, and inefficiency, and a robust integrated system from Fengding costs $80,000, the payback period is roughly 6-7 months. Every year after that, the $150,000 in saved costs flows directly to your bottom line. This doesn't even include the intangible benefits of improved safety, worker morale, and customer satisfaction from better-protected goods.
An integrated system is not an expense; it's a strategic investment in your factory's efficiency and resilience. Presenting the ROI in this comprehensive way turns a capital request into a compelling business growth proposal. (justifying automation investment, packaging line efficiency savings)
My Insights!
From my journey on the factory floor to building my own business, I've seen this transition firsthand. The decision to integrate automation is not just a technical one; it's a cultural and strategic shift. The most successful integrations I've witnessed happen when the factory manager partners with a supplier who speaks the language of production, not just sales. They understand that downtime is your enemy and that reliability is more valuable than a cheap price. A machine from a trusted partner becomes a seamless extension of your team, working tirelessly to secure your product and your profit. When you choose a partner, look for one with proven field experience, like the engineering teams behind leading brands, who can guide you through every step from planning to ROI realization.
Conclusion
Integrating an orbital stretch wrapper streamlines your line, boosts safety, and protects profits. It's a strategic upgrade with a clear ROI. For a durable solution, explore options from a trusted Orbital Stretch Wrapper partner.









